S³ – Safety sensor technology for service robots in production logistics and inpatient care

In short
In mobile service robotics, safety is a crucial aspect– especially when it comes to interaction with humans. The aim of the project is therefore to develop a sensor that will enable service robots to better detect their environment. Fraunhofer IPA is supporting the project by selecting the best sensor principle, further developing its 3D recognition software for objects and people, and by conducting practical tests on a mobile robot equipped with the sensor in a nursing home.
In detail
Mobile service robots are increasingly used in public areas where they interact and collaborate with people. In contrast to industrial environments, people who are completely inexperienced in handling machines are also faced with the robots. Especially in the health care sector, service robots can encounter people who are weak or whose mobility is impaired. For this reason, the machines require sophisticated sensor technology capable of recognizing dangerous situations and avoiding hazards. When planning safe robot actions, it is essential that the robot can differentiate between people and objects in its vicinity.
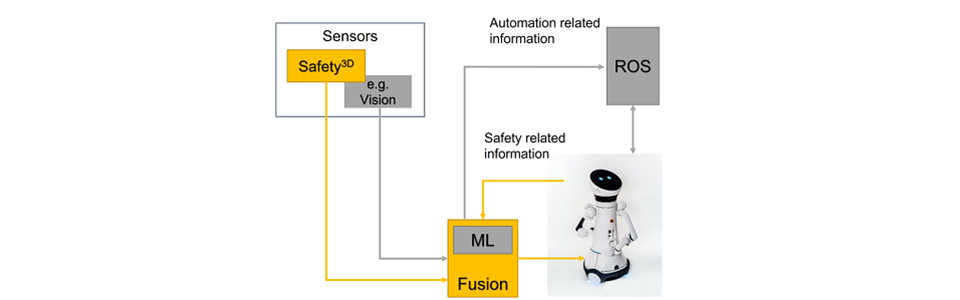
The goal of the project is to develop a corresponding 3D environmental sensor system for detecting objects and people and differentiating between them. To achieve this, Fraunhofer IPA is contributing its technical expertise in the field of sensor technology and software development. The IPA researchers started off by assisting in the requirements analysis, during which various fields of application of the robots were analyzed and the necessary properties of the sensor were derived. They also helped the partners to design of the sensor, as they have extensive expert knowledge in the field of imaging sensors.
Fraunhofer IPA has been successfully implementing research and industrial projects in the field of image processing for robotics for many years. In S³, therefore, existing methods for object, person and pose recognition are being further developed. In addition, methods of artificial intelligence are being used to enable service robots to understand situations and thus to react accordingly.
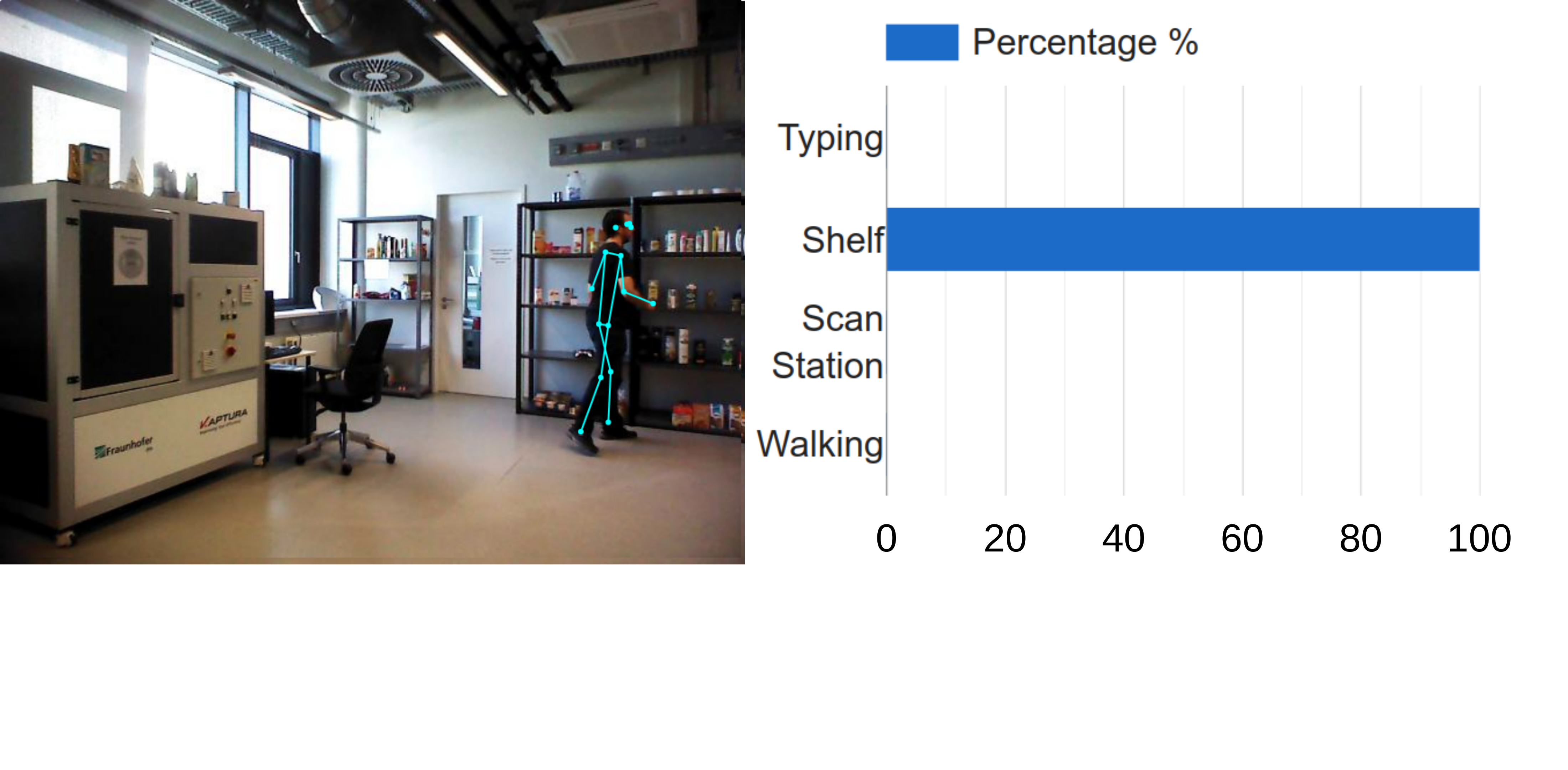
The project considers application scenarios from production logistics and stationary care. Practical tests on the sensor in the nursing context are carried out with the help of the Care-O-bot® 4 assistance robot. In doing so, the institute can draw on its longstanding experience in cooperation with care institutions.