ASARob: Attention-Sensitive Assistance Robot

In short
The aim of the research project “Attention-Sensitive Assistance Robot” (ASARob) was to develop new skills for interactive assistive robots - in particular, new image processing solutions - so that they can detect the state of attention of their human counterpart and, if appropriate, influence and direct it through their behavior. The skills were implemented on the assistive robot Care-O-bot® 4 which was used to guide a person safely and attentively through a public building to their destination.
In detail
If assistive robots such as Care-O-bot® 4 are to help humans in everyday life, they must be able to master basic interpersonal interaction skills. To provide agreeable and effective support, it is essential that the robot interacts with the human in a manner which is robust to errors and complies with expectations. To this end, skills were developed in the “Attention-Sensitive Assistance Robot” (ASARob) project that enable a robot to recognize where the user's attention is directed and what the user's intent is.
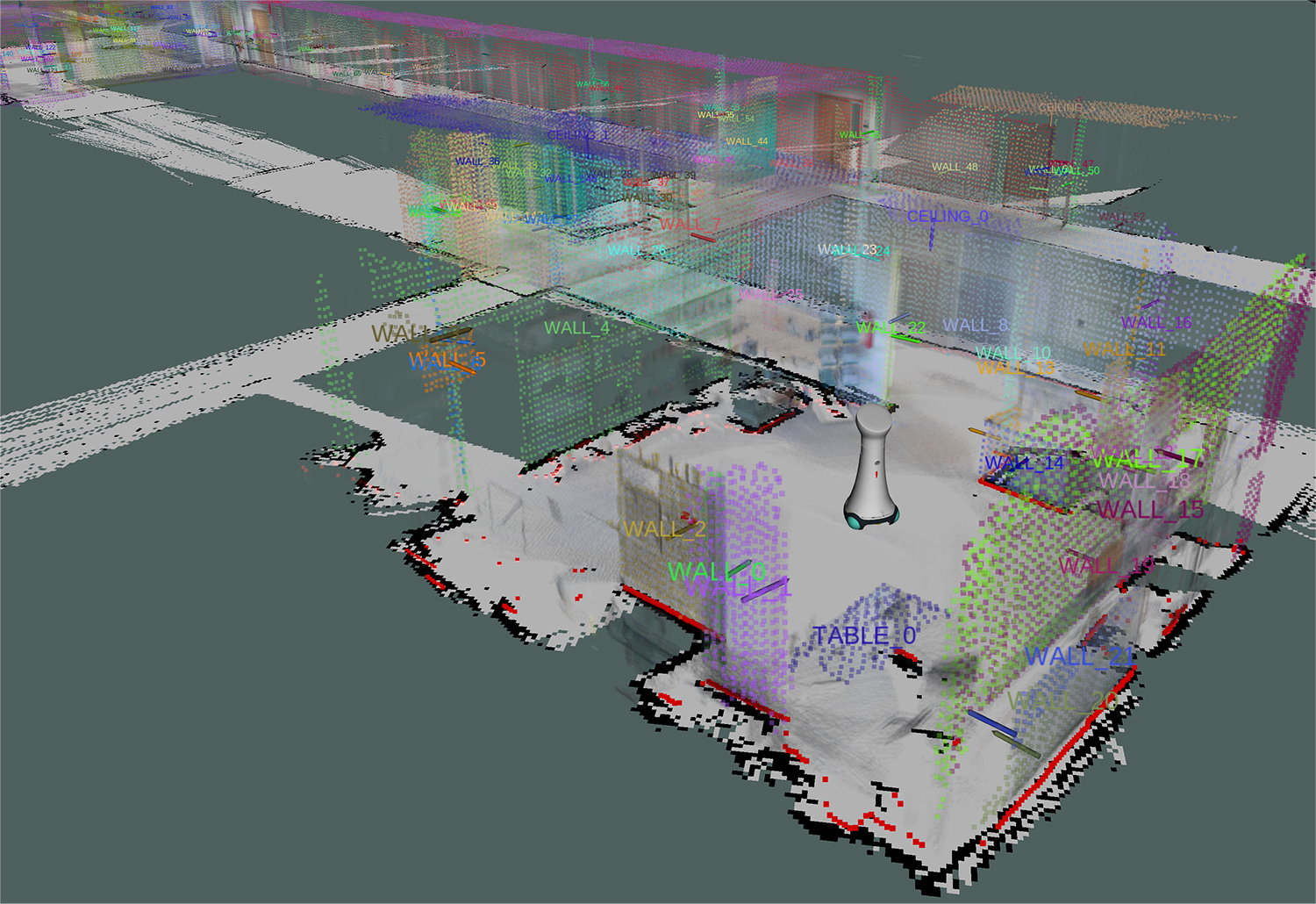
To support these capabilities, in the project, Fraunhofer IPA has developed an environment model that also includes semantics. These improve the understanding of the environmental information, which is available as a 3D point cloud, and recognize detected objects such as chairs, tables, or plants. This is made possible by new software modules that recognize and classify geometric shapes and derive corresponding spatial structures from them.
The technologies developed complement the range of human and activity recognition skills already available at IPA and now enable a robot to understand a scene holistically. The software components are ready for use and can be implemented singly or bundled for a wide range of applications.